Galvanometer Scheme on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A galvanometer is an
A galvanometer is an
 Modern galvanometers, of the D'Arsonval/Weston type, are constructed with a small pivoting coil of wire, called a spindle, in the field of a permanent magnet. The coil is attached to a thin pointer that traverses a calibrated scale. A tiny torsion spring pulls the coil and pointer to the zero position.
When a
Modern galvanometers, of the D'Arsonval/Weston type, are constructed with a small pivoting coil of wire, called a spindle, in the field of a permanent magnet. The coil is attached to a thin pointer that traverses a calibrated scale. A tiny torsion spring pulls the coil and pointer to the zero position.
When a
 Probably the largest use of galvanometers was of the D'Arsonval/Weston type used in analog meters in electronic equipment. Since the 1980s, galvanometer-type analog meter movements have been displaced by
Probably the largest use of galvanometers was of the D'Arsonval/Weston type used in analog meters in electronic equipment. Since the 1980s, galvanometer-type analog meter movements have been displaced by
 Moving coil type galvanometer mechanisms (called 'voice coils' by hard disk manufacturers) are used for controlling the ''head positioning'' servos in
Moving coil type galvanometer mechanisms (called 'voice coils' by hard disk manufacturers) are used for controlling the ''head positioning'' servos in
 Originally, the instruments relied on the Earth's magnetic field to provide the restoring force for the compass needle. These were called "tangent" galvanometers and had to be oriented before use. Later instruments of the "
Originally, the instruments relied on the Earth's magnetic field to provide the restoring force for the compass needle. These were called "tangent" galvanometers and had to be oriented before use. Later instruments of the "
 The early moving-magnet form of galvanometer had the disadvantage that it was affected by any magnets or iron masses near it, and its deflection was not linearly proportional to the current. In 1882
The early moving-magnet form of galvanometer had the disadvantage that it was affected by any magnets or iron masses near it, and its deflection was not linearly proportional to the current. In 1882

File:Sine and Tangent Galvanometer-MHS 98-IMG 3874-gradient.jpg, An 1850 Pouillet Tangent Galvanometer on display at
File:Galvanometer-MHS 229-IMG 3875-gradient.jpg, Galvanometer on display at
Galvanometer - Interactive Java Tutorial
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Selection of historic galvanometer
in the
The History Corner: The Galvanometer
by Nick Joyce and David Baker, April 1, 2008, Ass. of Physological Science. Retrieved February 26, 2022. {{Authority control Galvanometers Electrical instruments Historical scientific instruments
 A galvanometer is an
A galvanometer is an electromechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
measuring instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Est ...
for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit ...
s, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely.
A galvanometer works by deflecting a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a constant magnetic field. Galvanometers can be thought of as a kind of actuator.
Galvanometers came from the observation, first noted by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820, that a magnetic compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
's needle deflects when near a wire having electric current. They were the first instruments used to detect and measure small amounts of current. André-Marie Ampère, who gave mathematical expression to Ørsted's discovery, named the instrument after the Italian electricity researcher Luigi Galvani, who in 1791 discovered the principle of the frog galvanoscope – that electric current would make the legs of a dead frog jerk.
Galvanometers have been essential for the development of science and technology in many fields. For example, in the 1800s they enabled long-range communication through submarine cables, such as the earliest transatlantic telegraph cable
Transatlantic telegraph cables were undersea cables running under the Atlantic Ocean for telegraph communications. Telegraphy is now an obsolete form of communication, and the cables have long since been decommissioned, but telephone and data a ...
s, and were essential to discovering the electrical activity of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
and brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
, by their fine measurements of current.
Galvanometers have also been used as the display components of other kinds of analog meters (e.g., light meter
A light meter is a device used to measure the amount of light. In photography, a light meter (more correctly an exposure meter) is used to determine the proper exposure (photography), exposure for a photograph. The meter will include either a Di ...
s and VU meter
A volume unit (VU) meter or standard volume indicator (SVI) is a device displaying a representation of the signal level in audio equipment. The original design was proposed in the 1940 IRE paper, ''A New Standard Volume Indicator and Reference ...
s), capturing the outputs of these meters' sensors. Today, the main type of galvanometer still in use is the D'Arsonval/Weston type.
Operation
direct current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or eve ...
(DC) flows through the coil, the coil generates a magnetic field. This field acts against the permanent magnet. The coil twists, pushing against the spring, and moves the pointer. The hand points at a scale indicating the electric current. Careful design of the pole pieces ensures that the magnetic field is uniform so that the angular deflection of the pointer is proportional to the current. A useful meter generally contains a provision for damping the mechanical resonance of the moving coil and pointer, so that the pointer settles quickly to its position without oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
.
The basic sensitivity of a meter might be, for instance, 100 microamperes full scale (with a voltage drop of, say, 50 millivolts at full current). Such meters are often calibrated to read some other quantity that can be converted to a current of that magnitude. The use of current dividers, often called shunts, allows a meter to be calibrated to measure larger currents. A meter can be calibrated as a DC voltmeter if the resistance of the coil is known by calculating the voltage required to generate a full-scale current. A meter can be configured to read other voltages by putting it in a voltage divider circuit. This is generally done by placing a resistor in series with the meter coil. A meter can be used to read resistance by placing it in series with a known voltage (a battery) and an adjustable resistor. In a preparatory step, the circuit is completed and the resistor adjusted to produce full-scale deflection. When an unknown resistor is placed in series in the circuit the current will be less than full scale and an appropriately calibrated scale can display the value of the previously unknown resistor.
These capabilities to translate different kinds of electric quantities into pointer movements make the galvanometer ideal for turning the output of other sensors that output electricity (in some form or another), into something that can be read by a human.
Because the pointer of the meter is usually a small distance above the scale of the meter, parallax error can occur when the operator attempts to read the scale line that "lines up" with the pointer. To counter this, some meters include a mirror along with the markings of the principal scale. The accuracy of the reading from a mirrored scale is improved by positioning one's head while reading the scale so that the pointer and the reflection of the pointer are aligned; at this point, the operator's eye must be directly above the pointer and any parallax error has been minimized.
Uses
 Probably the largest use of galvanometers was of the D'Arsonval/Weston type used in analog meters in electronic equipment. Since the 1980s, galvanometer-type analog meter movements have been displaced by
Probably the largest use of galvanometers was of the D'Arsonval/Weston type used in analog meters in electronic equipment. Since the 1980s, galvanometer-type analog meter movements have been displaced by analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
s (ADCs) for many uses. A digital panel meter (DPM) contains an ADC and numeric display. The advantages of a digital instrument are higher precision and accuracy, but factors such as power consumption or cost may still favor the application of analog meter movements.
Modern uses
Most modern uses for the galvanometer mechanism are in positioning and control systems. Galvanometer mechanisms are divided into moving magnet and moving coil galvanometers; in addition, they are divided into ''closed-loop'' and ''open-loop'' - or ''resonant'' - types. ''Mirror'' galvanometer systems are used as beam positioning or beam steering elements in laser scanning systems. For example, for material processing with high-power lasers, closed loop mirror galvanometer mechanisms are used withservo
Servo may refer to:
Mechanisms
* Servomechanism, or servo, a device used to provide control of a desired operation through the use of feedback
** AI servo, an autofocus mode
** Electrohydraulic servo valve, an electrically operated valve that c ...
control systems. These are typically high power galvanometers and the newest galvanometers designed for beam steering applications can have frequency responses over 10 kHz with appropriate servo technology. Closed-loop mirror galvanometers are also used in similar ways in stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a lay ...
, laser sintering, laser engraving, laser beam welding
Laser beam welding (LBW) is a welding technique used to join pieces of metal or thermoplastics through the use of a laser. The beam provides a concentrated heat source, allowing for narrow, deep welds and high welding rates. The process is frequen ...
, laser TV
Laser color television (laser TV), or laser color video display, is a type of television that utilizes two or more individually modulated optical (laser) rays of different colors to produce a combined spot that is scanned and projected across the ...
s, laser display
A laser lighting display or laser light show involves the use of laser light to entertain an audience. A laser light show may consist only of projected laser beams set to music, or may accompany another form of entertainment, typically mus ...
s and in imaging applications such as retinal scanning with Optical Coherence Tomography
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging technique that uses low-coherence light to capture micrometer-resolution, two- and three-dimensional images from within optical scattering media (e.g., biological tissue). It is used for medica ...
(OCT) and Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy
Scanning laser ophthalmoscopy (SLO) is a method of examination of the eye. It uses the technique of confocal laser scanning microscopy for diagnostic imaging of the retina or cornea of the human eye.
As a method used to image the retina with a h ...
(SLO). Almost all of these galvanometers are of the moving magnet type. The closed loop is obtained measuring the position of the rotating axis with an infrared emitter and 2 photodiodes. This feedback is an analog signal.
Open loop, or resonant mirror galvanometers, are mainly used in some types of laser-based bar-code scanners, printing machines, imaging applications, military applications and space systems. Their non-lubricated bearings are especially of interest in applications that require functioning in a high vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
.
hard disk drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magne ...
s and CD/DVD players, in order to keep mass (and thus access times), as low as possible.
Past uses
A major early use for galvanometers was for finding faults in telecommunications cables. They were superseded in this application late in the 20th century bytime-domain reflectometer
A time-domain reflectometer (TDR) is an electronic instrument used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines by observing reflected waveforms.
It can be used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables (for example, twisted pa ...
s.
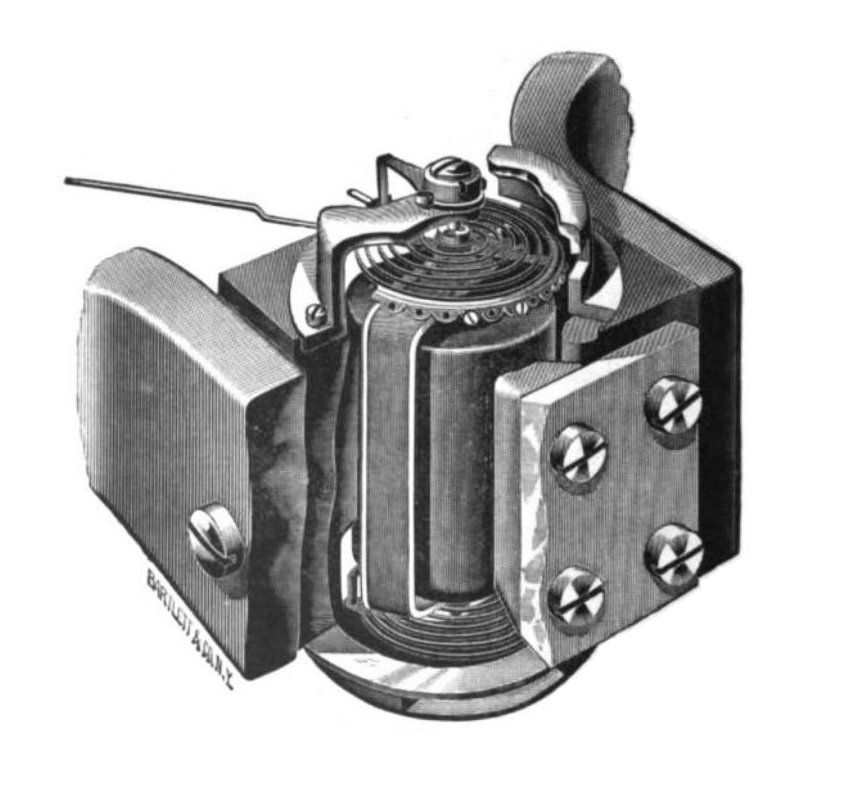
Galvanometer mechanisms were also used to get readings from photoresistor
A photoresistor (also known as a photocell, or light-dependent resistor, LDR, or photo-conductive cell) is a passive component that decreases resistance with respect to receiving luminosity (light) on the component's sensitive surface. The resi ...
s in the metering mechanisms of film cameras (as seen in the adjacent image).
In analog strip chart recorder
A chart recorder is an electromechanical device that records an electrical or mechanical input trend onto a piece of paper (the chart). Chart recorders may record several inputs using different color pens and may record onto strip charts or circ ...
s such as used in electrocardiographs, electroencephalographs and polygraph
A polygraph, often incorrectly referred to as a lie detector test, is a device or procedure that measures and records several physiological indicators such as blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and skin conductivity while a person is asked ...
s, galvanometer mechanisms were used to position the ''pen''. Strip chart recorders with galvanometer driven pens may have a full-scale frequency response of 100 Hz and several centimeters of deflection.
History
Hans Christian Ørsted
The deflection of amagnetic compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself with ...
needle by the current in a wire was first described by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820. The phenomenon was studied both for its own sake and as a means of measuring electric current.
Schweigger and Ampère
The earliest galvanometer was reported byJohann Schweigger
Johann Salomo Christoph Schweigger (8 April 1779 – 6 September 1857) was a German chemist, physicist, and professor of mathematics born in Erlangen.
J.S.C.Schweigger was the son of Friedrich Christian Lorenz Schweigger, professor of theologie ...
at the University of Halle
Martin Luther University of Halle-Wittenberg (german: Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg), also referred to as MLU, is a public, research-oriented university in the cities of Halle and Wittenberg and the largest and oldest university in ...
on 16 September 1820. André-Marie Ampère also contributed to its development. Early designs increased the effect of the magnetic field generated by the current by using multiple turns of wire. The instruments were at first called "multipliers" due to this common design feature. The term "galvanometer," in common use by 1836, was derived from the surname of Italian electricity researcher Luigi Galvani, who in 1791 discovered that electric current would make a dead frog's leg jerk.
Poggendorff and Thomson
 Originally, the instruments relied on the Earth's magnetic field to provide the restoring force for the compass needle. These were called "tangent" galvanometers and had to be oriented before use. Later instruments of the "
Originally, the instruments relied on the Earth's magnetic field to provide the restoring force for the compass needle. These were called "tangent" galvanometers and had to be oriented before use. Later instruments of the "astatic
The Astatic was a French cyclecar manufactured from 1920 to 1922 by Automobiles Astatic, Saint-Ouen, Seine, France.
Built at Saint-Ouen, the car was an attempt to market a vehicle with independent suspension
Independent suspension is any auto ...
" type used opposing magnets to become independent of the Earth's field and would operate in any orientation.
An early mirror galvanometer
A mirror galvanometer is an ammeter that indicates it has sensed an electric current by deflecting a light beam with a mirror. The beam of light projected on a scale acts as a long massless pointer. In 1826, Johann Christian Poggendorff devel ...
was invented in 1826 by Johann Christian Poggendorff
Johann Christian Poggendorff (29 December 1796 – 24 January 1877), was a German physicist born in Hamburg. By far the greater and more important part of his work related to electricity and magnetism. Poggendorff is known for his electrostatic ...
. An astatic galvanometer was invented by Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Associatio ...
in 1849; a more sensitive version of that device, the Thomson ''mirror galvanometer'', was patented in 1858 by William Thomson (Lord Kelvin). Thomson's design was able to detect very rapid current changes by using small magnets attached to a lightweight mirror, suspended by a thread, instead of a compass needle. The deflection of a light beam on the mirror greatly magnified the deflection induced by small currents. Alternatively, the deflection of the suspended magnets could be observed directly through a microscope.
Georg Ohm
The ability to measure quantitatively voltage and current allowedGeorg Ohm
Georg Simon Ohm (, ; 16 March 1789 – 6 July 1854) was a German physicist and mathematician. As a school teacher, Ohm began his research with the new electrochemical cell, invented by Italian scientist Alessandro Volta. Using equipment of his o ...
, in 1827, to formulate Ohm's Law – that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current through it.
D'Arsonval and Deprez
 The early moving-magnet form of galvanometer had the disadvantage that it was affected by any magnets or iron masses near it, and its deflection was not linearly proportional to the current. In 1882
The early moving-magnet form of galvanometer had the disadvantage that it was affected by any magnets or iron masses near it, and its deflection was not linearly proportional to the current. In 1882 Jacques-Arsène d'Arsonval
Jacques-Arsène d'Arsonval (8 June 1851 – 31 December 1940) was a French physician, physicist and inventor of the moving-coil D'Arsonval galvanometer and the thermocouple ammeter. D'Arsonval was an important contributor to the emerging field of ...
and Marcel Deprez
Marcel Deprez (12 December 1843 – 13 October 1918) was a French electrical engineer. He was born in Aillant-sur-Milleron. He died in Vincennes.
Biography
Deprez was born in Aillant-sur-Milleron in rural France and attended the School of Mines ...
developed a form with a stationary permanent magnet and a moving coil of wire, suspended by fine wires which provided both an electrical connection to the coil and the restoring torque to return to the zero position. An iron tube between the magnet's pole pieces defined a circular gap through which the coil rotated. This gap produced a consistent, radial magnetic field across the coil, giving a linear response throughout the instrument's range. A mirror attached to the coil deflected a beam of light to indicate the coil position. The concentrated magnetic field and delicate suspension made these instruments sensitive; d'Arsonval's initial instrument could detect ten microamperes.
Edward Weston


Edward Weston
Edward Henry Weston (March 24, 1886 – January 1, 1958) was a 20th-century American photographer. He has been called "one of the most innovative and influential American photographers..." and "one of the masters of 20th century photography." ...
extensively improved the design of the galvanometer. He substituted the fine wire suspension with a pivot and provided restoring torque and electrical connections through spiral springs rather than through the traditional wristwatch balance wheel
A balance wheel, or balance, is the timekeeping device used in mechanical watches and small clocks, analogous to the pendulum in a pendulum clock. It is a weighted wheel that rotates back and forth, being returned toward its center position by a ...
hairspring. He developed a method of stabilizing the magnetic field of the permanent magnet, so the instrument would have consistent accuracy over time. He replaced the light beam and mirror with a knife-edge pointer that could be read directly. A mirror under the pointer, in the same plane as the scale, eliminated parallax observation error. To maintain the field strength, Weston's design used a very narrow circumferential slot through which the coil moved, with a minimal air-gap. This improved linearity of pointer deflection with respect to coil current. Finally, the coil was wound on a light-weight form made of conductive metal, which acted as a damper. By 1888, Edward Weston had patented and brought out a commercial form of this instrument, which became a standard electrical equipment component. It was known as a "portable" instrument because it was affected very little by mounting position or by transporting it from place to place. This design is almost universally used in moving-coil meters today.
Initially, laboratory instruments relying on the Earth's own magnetic field to provide restoring force for the pointer, galvanometers were developed into compact, rugged, sensitive portable instruments essential to the development of electro-technology.
Taut-band movement
The taut-band movement is a modern development of the D'Arsonval-Weston movement. The jewel pivots and hairsprings are replaced by tiny strips of metal under tension. Such a meter is more rugged for field use.Types
There is broadly two types of galvanometers. Some galvanometers use a solid pointer on a scale to show measurements; other very sensitive types use a miniature mirror and a beam of light to provide mechanical amplification of low-level signals.Tangent galvanometer
A tangent galvanometer is an earlymeasuring instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Est ...
used for the measurement of electric current. It works by using a compass
A compass is a device that shows the cardinal directions used for navigation and geographic orientation. It commonly consists of a magnetized needle or other element, such as a compass card or compass rose, which can pivot to align itself wit ...
needle to compare a magnetic field generated by the unknown current to the magnetic field of the Earth. It gets its name from its operating principle, the tangent law of magnetism, which states that the tangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. Mo ...
of the angle a compass needle makes is proportional to the ratio of the strengths of the two perpendicular magnetic fields. It was first described by Johan Jakob Nervander in 1834.
A tangent galvanometer consists of a coil of insulated copper wire wound on a circular non-magnetic frame. The frame is mounted vertically on a horizontal base provided with levelling screws. The coil can be rotated on a vertical axis passing through its centre. A compass box is mounted horizontally at the centre of a circular scale. It consists of a tiny, powerful magnetic needle pivoted at the centre of the coil. The magnetic needle is free to rotate in the horizontal plane. The circular scale is divided into four quadrants. Each quadrant is graduated from 0° to 90°. A long thin aluminium pointer is attached to the needle at its centre and at right angle to it. To avoid errors due to parallax, a plane mirror is mounted below the compass needle.
In operation, the instrument is first rotated until the magnetic field of the Earth, indicated by the compass needle, is parallel with the plane of the coil. Then the unknown current is applied to the coil. This creates a second magnetic field on the axis of the coil, perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic field. The compass needle responds to the vector sum
In mathematics, physics, and engineering, a Euclidean vector or simply a vector (sometimes called a geometric vector or spatial vector) is a geometric object that has magnitude (or length) and direction. Vectors can be added to other vectors a ...
of the two fields and deflects to an angle equal to the tangent of the ratio of the two fields. From the angle read from the compass's scale, the current could be found from a table. The current supply wires have to be wound in a small helix, like a pig's tail, otherwise the field due to the wire will affect the compass needle and an incorrect reading will be obtained.
Musée d'histoire des sciences de la Ville de Genève
The ''Musée d'histoire des sciences de la Ville de Genève'' (Museum of the History of Science of the City of Geneva) is a small museum in Switzerland dedicated to the history of science.
Location
The museum is located in the ''Villa Bartholon ...
File:Western Union standard galvanometer.jpg, alt=Drawing. The prominent feature is a vertical ring seen from the front. It is mounted on a horizontal disk that has electrical connectors. A horizontal compass is mounted at the center of the ring., Tangent galvanometer made by J. H. Bunnell Co. around 1890.
File:Tangent galvanometer Philip-Harris top1.jpg, alt=Photograph. The most prominent feature is a horizontal circular compass case that is seen from above. The compass is centered inside of a black ring with a square cross-section. The compass and ring are supported on a brass tripod that has leveling screws as its feet., Top view of a tangent galvanometer made about 1950. The indicator needle of the compass is perpendicular to the shorter, black magnetic needle.
Theory
The galvanometer is oriented so that the plane of the coil is vertical and aligned along parallel to the horizontal component of the Earth's magnetic field (i.e. parallel to the local "magnetic meridian"). When an electric current flows through the galvanometer coil, a second magnetic field is created. At the center of the coil, where the compass needle is located, the coil's field is perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The magnitude of the coil's field is: : where is the current in amperes, is the number of turns of the coil and is the radius of the coil. These two perpendicular magnetic fields add vectorially, and the compass needle points along the direction of their resultant . The current in the coil causes the compass needle to rotate by an angle : : From tangent law, , i.e. : or : or , where is called the Reduction Factor of the tangent galvanometer. One problem with the tangent galvanometer is that its resolution degrades at both high currents and low currents. The maximum resolution is obtained when the value of is 45°. When the value of is close to 0° or 90°, a large percentage change in the current will only move the needle a few degrees.Geomagnetic field measurement
A tangent galvanometer can also be used to measure the magnitude of the horizontal component of the geomagnetic field. When used in this way, a low-voltage power source, such as a battery, is connected in series with arheostat
A potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat.
The measuring instrume ...
, the galvanometer, and an ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit ...
. The galvanometer is first aligned so that the coil is parallel to the geomagnetic field, whose direction is indicated by the compass when there is no current through the coils. The battery is then connected and the rheostat is adjusted until the compass needle deflects 45 degrees from the geomagnetic field, indicating that the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the coil is the same as that of the horizontal component of the geomagnetic field. This field strength can be calculated from the current as measured by the ammeter, the number of turns of the coil, and the radius of the coils.
Astatic galvanometer
Unlike the tangent galvanometer, the ''astatic galvanometer'' does not use the Earth's magnetic field for measurement, so it does not need to be oriented with respect to the Earth's field, making it easier to use. Developed byLeopoldo Nobili
Leopoldo Nobili, born on 5 July 1784 in Trassilico (Toscana) and died on 22 August 1835 in Florence, was an Italian physicist who invented a number of instruments critical to investigating thermodynamics and electrochemistry.
Born Trassilico, Gar ...
in 1825, it consists of two magnetized needles parallel to each other but with the magnetic poles reversed. These needles are suspended by a single silk thread. The lower needle is inside a vertical current sensing coil of wire and is deflected by the magnetic field created by the passing current, as in the tangent galvanometer above. The purpose of the second needle is to cancel the dipole moment of the first needle, so the suspended armature has no net magnetic dipole moment, and thus is not affected by the earth's magnetic field. The needle's rotation is opposed by the torsional elasticity of the suspension thread, which is proportional to the angle.
Musée d'histoire des sciences de la Ville de Genève
The ''Musée d'histoire des sciences de la Ville de Genève'' (Museum of the History of Science of the City of Geneva) is a small museum in Switzerland dedicated to the history of science.
Location
The museum is located in the ''Villa Bartholon ...
File:Astatic Galvanometer brass and ivory.jpg, Detail of an astatic galvanometer.
Mirror galvanometer
To achieve higher sensitivity to detect extremely small currents, themirror galvanometer
A mirror galvanometer is an ammeter that indicates it has sensed an electric current by deflecting a light beam with a mirror. The beam of light projected on a scale acts as a long massless pointer. In 1826, Johann Christian Poggendorff devel ...
substitutes a lightweight mirror for the pointer. It consists of horizontal magnets suspended from a fine fiber, inside a vertical coil of wire, with a mirror attached to the magnets. A beam of light reflected from the mirror falls on a graduated scale across the room, acting as a long mass-less pointer. The mirror galvanometer was used as the receiver in the first trans-Atlantic submarine telegraph cables in the 1850s, to detect the extremely faint pulses of current after their thousand-mile journey under the Atlantic. In a device called an oscillograph
An oscilloscope (informally a scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying electrical voltages as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. The main purposes are to display repetiti ...
, the moving beam of light is used, to produce graphs of current versus time, by recording measurements on photographic film. The string galvanometer
A string galvanometer is a sensitive fast-responding measuring instrument that uses a single fine filament of wire suspended in a strong magnetic field to measure small currents. In use, a strong light source is used to illuminate the fine filament ...
is a type of mirror galvanometer so sensitive that it was used to make the first electrocardiogram of the electrical activity of the human heart.
Ballistic galvanometer
A ballistic galvanometer is a type of sensitive galvanometer for measuring the quantity ofcharge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
discharged through it. It is an integrator, by virtue of the long time constant In physics and engineering, the time constant, usually denoted by the Greek letter (tau), is the parameter characterizing the response to a step input of a first-order, linear time-invariant (LTI) system.Concretely, a first-order LTI system is a s ...
of its response, unlike a current-measuring galvanometer. The moving part has a large moment of inertia that gives it an oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
period long enough to make the integrated measurement. It can be either of the moving coil or moving magnet type; commonly it is a mirror galvanometer.
See also
* Vibration galvanometer *Thermo galvanometer
The thermo-galvanometer is an instrument for measuring small electric currents. It was invented by William Duddell about 1900. The following is a description of the instrument taken from a trade catalog of Cambridge Scientific Instrument Company
...
*String galvanometer
A string galvanometer is a sensitive fast-responding measuring instrument that uses a single fine filament of wire suspended in a strong magnetic field to measure small currents. In use, a strong light source is used to illuminate the fine filament ...
*History of electrochemistry Electrochemistry, a branch of chemistry, went through several changes during its evolution from early principles related to magnets in the early 16th and 17th centuries, to complex theories involving conductivity, electric charge and mathematical me ...
References
External links
Galvanometer - Interactive Java Tutorial
National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
Selection of historic galvanometer
in the
Virtual Laboratory The online project Virtual Laboratory. Essays and Resources on the Experimentalization of Life, 1830-1930, located at the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science, is dedicated to research in the history of the experimentalization of life. T ...
of the Max Planck Institute for the History of Science
The Max Planck Institute for the History of Science (German: Max-Planck-Institut für Wissenschaftsgeschichte) is a scientific research institute founded in March 1994. It is dedicated to addressing fundamental questions of the history of knowledg ...
The History Corner: The Galvanometer
by Nick Joyce and David Baker, April 1, 2008, Ass. of Physological Science. Retrieved February 26, 2022. {{Authority control Galvanometers Electrical instruments Historical scientific instruments